Product Description
Viair 444C Black Dual Pack Air Compressor Air Ride Bagged Compressor
Viair 480c Chrome Air Compressor
The Viair 480C is a truly rated, constant duty 200 CHINAMFG compressor. This compressor is capable of filling a 5 gallon tank from 165 to 200 CHINAMFG in only 2 minutes and 20 seconds. It features horizontal cooling fins and a trapezoidal head design, a standard 3/8″ stainless steel braided leader hose with 3/8″ NPT inline check valve and insulated wiring. This product includes all necessary installation components, instructions and insulated wiring with connectors.
Specifications: Features:
- Voltage: 12 Volts – Permanent Magnetic Motor
- Max Amperage: 19 Amps – Stainless Steel Valves
- Max Duty Cycle: 100% @ 100 CHINAMFG – Moisture & Dust Resistant
- Max Working Pressure: 200 CHINAMFG – Stainless Steel 3/8″ Leader Hose
- Length: 10.28 in (261 mm) – Insulated Wiring with Connections
- Width: 4.17 in (106 mm) – Mounting Plates with Vibration Isolators
- Height: 6.6 in (167.7 mm) – Intake Filter Assembly
- Weight: 11 lbs (4.99 Kg) – Installation Instructions
- Features:
444 is a truly rated, 200 PSI-rated compressor. It features horizontal cooling fins and a trapezoidal head design, a standard 1/4″ stainless steel braided leader hose with 1/4″ NPT inline check valve and insulated wiring.
Included Parts:
– Check Valve
– Vibration Isolators
– Mounting Hardware
– Stainless Steel Braided Leader Hose
– Air Line for Remote Mount Air Filter
– Remote Mount Air Filter Assembly
– (2) Replacement Air Filter Elements
– Installation Instructions
Specifications:
– 12-Volt
– Permanent Magnetic Motor
– Duty Cycle: 100% @ 100 PSI
– Max. Working Pressure: 200 PSI
– Max. Air Tank Size: 5.0 Gallon
– Max. Amp Draw: 23 Amps
– Dimensions: 10.6″L x 4″W x 6.87″H
– Net Weight: 10.80 lbs.
Included Parts: Check Valve,Vibration Isolators,Mounting Hardware,Stainless Steel Braided Leader Hose,Direct Air Filter Assembly,(2) Replacement Air Filter Elements,Installation Instructions
Specifications:
| The performance data | |||||
| PSI | CFM | A | BAR | LRM | A |
| 0 | 1.76 | 10 | 0 | 50 | 10 |
| 10 | 1.66 | 12 | 1 | 46 | 13 |
| 20 | 1.59 | 13 | 2 | 43 | 14 |
| 30 | 1.52 | 14 | 3 | 40.5 | 17 |
| 40 | 1.45 | 16 | 4 | 38.5 | 18 |
| 50 | 1.41 | 17 | 5 | 35.5 | 19 |
| 60 | 1.34 | 18 | 6 | 33 | 19 |
| 70 | 1.27 | 18 | 7 | 31.5 | 19 |
| 80 | 1.2 | 19 | 8 | 29.5 | 20 |
| 90 | 1.16 | 19 | 9 | 27 | 20 |
| 100 | 1.13 | 19 | 10 | 25 | 19 |
| 110 | 1.06 | 20 | 11 | 23 | 19 |
| 120 | 1.02 | 20 | 12 | 20.5 | 19 |
| 130 | 0.95 | 20 | 13 | 15 | 18 |
| 140 | 0.92 | 19 | 14 | 15.5 | 18 |
| 150 | 0.85 | 19 | |||
| 160 | 0.81 | 19 | |||
| 170 | 0.74 | 19 | |||
| 180 | 0.7 | 19 | |||
| 190 | 0.63 | 18 | |||
| 200 | 0.56 | 18 | Supply Voltage: 13.8 Volts | ||
| Fill Rates | |
| 2.5 Gallon Tank | Fill Rate |
| 0 To 145 PSI | 2 Min. 29 Sec. |
| 110 To 145 PSI | 57 Sec. |
| 0 to 200 PSI | 5 Min. 02 Sec. |
| 165 to 200 PSI | 1 Min. 23 Sec. |
| 5.0 Gallon Tank | Fill Rate |
| 0 To 145 PSI | 6 Min. 02 Sec. |
| 110 To 145 PSI | 1 Min. 55 Sec. |
| 0 to 200 PSI | 10 Min. 08 Sec. |
| 165 to 200 PSI | 2 Min. 20 Sec. |
Air compressor Application: Air Suspension, Air Horn, Sweeper, Air Vending Machine, Air Controlled Door, Air Chair, Air Brake Assist, Air Locker, Agricultural Machinery, Industrial and Medical Applications, etc.
| Classification: | Variable Capacity |
|---|---|
| Job Classification: | Rotary Type |
| Transmission Power: | Turbine |
| Cooling Method: | Air-cooled |
| Cylinder Arrangement Mode: | Duplex |
| Cylinder Stage: | Double Stages |
| Samples: |
US$ 69/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
What are the differences between stationary and portable air compressors?
Stationary and portable air compressors are two common types of air compressors with distinct features and applications. Here are the key differences between them:
1. Mobility:
The primary difference between stationary and portable air compressors is their mobility. Stationary air compressors are designed to be permanently installed in a fixed location, such as a workshop or a factory. They are typically larger, heavier, and not easily movable. On the other hand, portable air compressors are smaller, lighter, and equipped with handles or wheels for easy transportation. They can be moved from one location to another, making them suitable for jobsites, construction sites, and other mobile applications.
2. Power Source:
Another difference lies in the power source used by stationary and portable air compressors. Stationary compressors are usually powered by electricity, as they are designed for continuous operation in a fixed location with access to power outlets. They are connected to the electrical grid or have dedicated wiring. In contrast, portable compressors are available in various power options, including electric, gasoline, and diesel engines. This versatility allows them to operate in remote areas or sites without readily available electricity.
3. Tank Capacity:
Tank capacity is also a distinguishing factor between stationary and portable air compressors. Stationary compressors often have larger storage tanks to store compressed air for extended periods. The larger tanks enable them to deliver a continuous and steady supply of compressed air for longer durations without the need for frequent cycling. Portable compressors, due to their compact size and portability, generally have smaller tank capacities, which may be sufficient for intermittent or smaller-scale applications.
4. Performance and Output:
The performance and output capabilities of stationary and portable air compressors can vary. Stationary compressors are typically designed for high-volume applications that require a consistent and continuous supply of compressed air. They often have higher horsepower ratings, larger motor sizes, and higher air delivery capacities. Portable compressors, while generally offering lower horsepower and air delivery compared to their stationary counterparts, are still capable of delivering sufficient air for a range of applications, including pneumatic tools, inflation tasks, and light-duty air-powered equipment.
5. Noise Level:
Noise level is an important consideration when comparing stationary and portable air compressors. Stationary compressors, being larger and built for industrial or commercial settings, are often equipped with noise-reducing features such as sound insulation and vibration dampening. They are designed to operate at lower noise levels, which is crucial for maintaining a comfortable working environment. Portable compressors, while efforts are made to reduce noise, may produce higher noise levels due to their compact size and portability.
6. Price and Cost:
Stationary and portable air compressors also differ in terms of price and cost. Stationary compressors are generally more expensive due to their larger size, higher power output, and industrial-grade construction. They often require professional installation and may involve additional costs such as electrical wiring and system setup. Portable compressors, being smaller and more versatile, tend to have a lower upfront cost. They are suitable for individual users, contractors, and small businesses with budget constraints or flexible air supply needs.
When selecting between stationary and portable air compressors, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the intended application, such as mobility, power source availability, air demands, and noise considerations. Understanding these differences will help in choosing the appropriate type of air compressor for the intended use.
.webp)
What is the energy efficiency of modern air compressors?
The energy efficiency of modern air compressors has significantly improved due to advancements in technology and design. Here’s an in-depth look at the energy efficiency features and factors that contribute to the efficiency of modern air compressors:
Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Technology:
Many modern air compressors utilize Variable Speed Drive (VSD) technology, also known as Variable Frequency Drive (VFD). This technology allows the compressor motor to adjust its speed according to the compressed air demand. By matching the motor speed to the required airflow, VSD compressors can avoid excessive energy consumption during periods of low demand, resulting in significant energy savings compared to fixed-speed compressors.
Air Leakage Reduction:
Air leakage is a common issue in compressed air systems and can lead to substantial energy waste. Modern air compressors often feature improved sealing and advanced control systems to minimize air leaks. By reducing air leakage, the compressor can maintain optimal pressure levels more efficiently, resulting in energy savings.
Efficient Motor Design:
The motor of an air compressor plays a crucial role in its energy efficiency. Modern compressors incorporate high-efficiency electric motors that meet or exceed established energy efficiency standards. These motors are designed to minimize energy losses and operate more efficiently, reducing overall power consumption.
Optimized Control Systems:
Advanced control systems are integrated into modern air compressors to optimize their performance and energy consumption. These control systems monitor various parameters, such as air pressure, temperature, and airflow, and adjust compressor operation accordingly. By precisely controlling the compressor’s output to match the demand, these systems ensure efficient and energy-saving operation.
Air Storage and Distribution:
Efficient air storage and distribution systems are essential for minimizing energy losses in compressed air systems. Modern air compressors often include properly sized and insulated air storage tanks and well-designed piping systems that reduce pressure drops and minimize heat transfer. These measures help to maintain a consistent and efficient supply of compressed air throughout the system, reducing energy waste.
Energy Management and Monitoring:
Some modern air compressors feature energy management and monitoring systems that provide real-time data on energy consumption and performance. These systems allow operators to identify energy inefficiencies, optimize compressor settings, and implement energy-saving practices.
It’s important to note that the energy efficiency of an air compressor also depends on factors such as the specific model, size, and application. Manufacturers often provide energy efficiency ratings or specifications for their compressors, which can help in comparing different models and selecting the most efficient option for a particular application.
Overall, modern air compressors incorporate various energy-saving technologies and design elements to enhance their efficiency. Investing in an energy-efficient air compressor not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to sustainability efforts by minimizing energy consumption and reducing carbon emissions.
.webp)
How do oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ?
Oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ in terms of their lubrication systems and the presence of oil in their operation. Here are the key differences:
Oil-Lubricated Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-lubricated air compressors use oil for lubricating the moving parts, such as pistons, cylinders, and bearings. The oil forms a protective film that reduces friction and wear, enhancing the compressor’s efficiency and lifespan.
2. Performance: Oil-lubricated compressors are known for their smooth and quiet operation. The oil lubrication helps reduce noise levels and vibration, resulting in a more comfortable working environment.
3. Maintenance: These compressors require regular oil changes and maintenance to ensure the proper functioning of the lubrication system. The oil filter may need replacement, and the oil level should be regularly checked and topped up.
4. Applications: Oil-lubricated compressors are commonly used in applications that demand high air quality and continuous operation, such as industrial settings, workshops, and manufacturing facilities.
Oil-Free Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-free air compressors do not use oil for lubrication. Instead, they utilize alternative materials, such as specialized coatings, self-lubricating materials, or water-based lubricants, to reduce friction and wear.
2. Performance: Oil-free compressors generally have a higher airflow capacity, making them suitable for applications where a large volume of compressed air is required. However, they may produce slightly more noise and vibration compared to oil-lubricated compressors.
3. Maintenance: Oil-free compressors typically require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated ones. They do not need regular oil changes or oil filter replacements. However, it is still important to perform routine maintenance tasks such as air filter cleaning or replacement.
4. Applications: Oil-free compressors are commonly used in applications where air quality is crucial, such as medical and dental facilities, laboratories, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications. They are also favored for portable and consumer-grade compressors.
When selecting between oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors, consider the specific requirements of your application, including air quality, noise levels, maintenance needs, and expected usage. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and lubrication to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the air compressor.


editor by CX 2023-10-11
China manufacturer E53 Air Suspension Pump BMW E65 / E66 E39 2 Corner 37221092349 4154031000 BMW Air Suspension Compressor 12v air compressor
Product Description
E53 Air Suspension Pump BMW E65 / E66 E39 2 Corner 4154571,,,
2008, 2009, 2571, 2011, 2012
| Reference OE/OEM Number: | ||
| 37206789450 | 37.20-6 789 450 | |
| 37206864215 | 37.20-6 864 215 | |
| 37206794465 | 37.20-6 794 465 | |
| 37206789165 | 37.20-6 789 165 | |
| 37206784137 | 37.20-6 784 137 | |
| 37206875176 | 37.20-6 875 176 | |
| This items can be installed in the following vehicles: | ||
| BMW F11 Touring >2009 ,BMW 7 Series F01/F02/F04 Air Suspension Compressor |
||
| BMW F11 LCI Touring >2012,BMW 5 Series F07/F11 Air Suspension Compressor | ||
For BMW 5 Series F11 Estate 2009-2018;
Models:
518 d , 520d , 520d xDrive , 520i , 523i ,
525d , 525d xDrive , 528i , 528i xDrive ,
530d , 530d xDrive , 530i , 535d , 535d xDrive ,
535i , 535i xDrive , 550i & M 550d xDrive .
For BMW 5 Series Gran Turismo F07 Hatchback 2009-2018;
Models:
520d, 528i, 530d, 530d xDrive, 535d, 535d xDrive, 535i, 535i xDrive, 550i & 550i xDrive.
This Air Compressor Fits for the following cars:
| OEM | Car Make | Model | Type | Bodystyle | Tyep | Engine |
| 37206789450 | BMW | 5 Series | 520d | Estate | 520d | 1995ccm 163HP 120KW (Diesel) |
| 37206864215 | BMW | 5 Series | 520d | Estate | 520d | 1995ccm 184HP 135KW (Diesel) |
| 37206794465 | BMW | 5 Series | 523i | Estate | 523i | 2497ccm 204HP 150KW (Petrol) |
| 37206789165 | BMW | 5 Series | 523i | Estate | 523i | 2996ccm 204HP 150KW (Petrol) |
| 37206784137 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d | Estate | 525d | 2993ccm 204HP 150KW (Diesel) |
| 37206875176 | BMW | 5 Series | 528i | Estate | 528i | 2996ccm 258HP 190KW (Petrol) |
| BMW | 5 Series | 530d | Estate | 530d | 2993ccm 245HP 180KW (Diesel) | |
| BMW | 5 Series | 535d | Estate | 535d | 2993ccm 299HP 220KW (Diesel) | |
| BMW | 5 Series | 535i | Estate | 535i | 2979ccm 306HP 225KW (Petrol) | |
| BMW | 5 Series | 520d | Estate | 520d | 1995ccm 163HP 120KW (Diesel) | |
| BMW | 5 Series | 520d | Estate | 520d | 1995ccm 184HP 135KW (Diesel) | |
| BMW | 5 Series | 520i | Estate | 520i | 1997ccm 163HP 120KW (Petrol) | |
| 37.20-6 789 450 | BMW | 5 Series | 520i | Estate | 520i | 1997ccm 184HP 135KW (Petrol) |
| 37.20-6 864 215 | BMW | 5 Series | 523i | Estate | 523i | 2497ccm 204HP 150KW (Petrol) |
| 37.20-6 794 465 | BMW | 5 Series | 523i | Estate | 523i | 2996ccm 204HP 150KW (Petrol) |
| 37.20-6 789 165 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d | Estate | 525d | 1995ccm 211HP 155KW (Diesel) |
| 37.20-6 784 137 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d | Estate | 525d | 1995ccm 218HP 160KW (Diesel) |
| 37.20-6 875 176 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d | Estate | 525d | 2993ccm 204HP 150KW (Diesel) |
| 37206789450 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d xDrive | Estate | 525d xDrive | 1995ccm 211HP 155KW (Diesel) |
| 37206864215 | BMW | 5 Series | 525d xDrive | Estate | 525d xDrive | 1995ccm 218HP 160KW (Diesel) |
| Material: | Rubber and Aluminum, Aluminum and Steel |
|---|---|
| Position: | Rear |
| OEM: | No |
| Type: | Air Suspension Compressor |
| Rated Voltage: | 12V |
| Maximum Current: | 35A |
| Samples: |
US$ 199/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for shipbuilding and maritime applications?
Air compressors are widely used in shipbuilding and maritime applications for a variety of tasks and operations. The maritime industry relies on compressed air for numerous essential functions. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are employed in shipbuilding and maritime applications:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Air compressors are extensively used to power pneumatic tools and equipment in shipbuilding and maritime operations. Pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches, drills, grinders, sanders, and chipping hammers require compressed air to function. The versatility and power provided by compressed air make it an ideal energy source for heavy-duty tasks, maintenance, and construction activities in shipyards and onboard vessels.
2. Painting and Surface Preparation:
Air compressors play a crucial role in painting and surface preparation during shipbuilding and maintenance. Compressed air is used to power air spray guns, sandblasting equipment, and other surface preparation tools. Compressed air provides the force necessary for efficient and uniform application of paints, coatings, and protective finishes, ensuring the durability and aesthetics of ship surfaces.
3. Pneumatic Actuation and Controls:
Air compressors are employed in pneumatic actuation and control systems onboard ships. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic valves, actuators, and control devices that regulate the flow of fluids, control propulsion systems, and manage various shipboard processes. Pneumatic control systems offer reliability and safety advantages in maritime applications.
4. Air Start Systems:
In large marine engines, air compressors are used in air start systems. Compressed air is utilized to initiate the combustion process in the engine cylinders. The compressed air is injected into the cylinders to turn the engine’s crankshaft, enabling the ignition of fuel and starting the engine. Air start systems are commonly found in ship propulsion systems and power generation plants onboard vessels.
5. Pneumatic Conveying and Material Handling:
In shipbuilding and maritime operations, compressed air is used for pneumatic conveying and material handling. Compressed air is utilized to transport bulk materials, such as cement, sand, and grain, through pipelines or hoses. Pneumatic conveying systems enable efficient and controlled transfer of materials, facilitating construction, cargo loading, and unloading processes.
6. Air Conditioning and Ventilation:
Air compressors are involved in air conditioning and ventilation systems onboard ships. Compressed air powers air conditioning units, ventilation fans, and blowers, ensuring proper air circulation, cooling, and temperature control in various ship compartments, cabins, and machinery spaces. Compressed air-driven systems contribute to the comfort, safety, and operational efficiency of maritime environments.
These are just a few examples of how air compressors are utilized in shipbuilding and maritime applications. Compressed air’s versatility, reliability, and convenience make it an indispensable energy source for various tasks and systems in the maritime industry.
.webp)
How are air compressors utilized in pneumatic tools?
Air compressors play a crucial role in powering and operating pneumatic tools. Here’s a detailed explanation of how air compressors are utilized in pneumatic tools:
Power Source:
Pneumatic tools rely on compressed air as their power source. The air compressor generates and stores compressed air, which is then delivered to the pneumatic tool through a hose or piping system. The compressed air provides the force necessary for the tool to perform various tasks.
Air Pressure Regulation:
Air compressors are equipped with pressure regulation systems to control the output pressure of the compressed air. Different pneumatic tools require different air pressure levels to operate optimally. The air compressor’s pressure regulator allows users to adjust the output pressure according to the specific requirements of the pneumatic tool being used.
Air Volume and Flow:
Air compressors provide a continuous supply of compressed air, ensuring a consistent air volume and flow rate for pneumatic tools. The air volume is typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and determines the tool’s performance capabilities. Higher CFM ratings indicate that the pneumatic tool can deliver more power and operate at a faster rate.
Tool Actuation:
Pneumatic tools utilize compressed air to actuate their mechanical components. For example, an air-powered impact wrench uses compressed air to drive the tool’s internal hammer mechanism, generating high torque for fastening or loosening bolts and nuts. Similarly, air-powered drills, sanders, nail guns, and spray guns rely on compressed air to power their respective operations.
Versatility:
One of the significant advantages of pneumatic tools is their versatility, and air compressors enable this flexibility. A single air compressor can power a wide range of pneumatic tools, eliminating the need for separate power sources for each tool. This makes pneumatic tools a popular choice in various industries, such as automotive, construction, manufacturing, and woodworking.
Portability:
Air compressors come in different sizes and configurations, offering varying degrees of portability. Smaller portable air compressors are commonly used in applications where mobility is essential, such as construction sites or remote locations. The portability of air compressors allows pneumatic tools to be used in various work environments without the constraints of being tethered to a fixed power source.
Overall, air compressors are integral to the functionality and operation of pneumatic tools. They provide the necessary power, air pressure regulation, and continuous airflow required for pneumatic tools to perform a wide range of tasks efficiently and effectively.
.webp)
How do oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ?
Oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ in terms of their lubrication systems and the presence of oil in their operation. Here are the key differences:
Oil-Lubricated Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-lubricated air compressors use oil for lubricating the moving parts, such as pistons, cylinders, and bearings. The oil forms a protective film that reduces friction and wear, enhancing the compressor’s efficiency and lifespan.
2. Performance: Oil-lubricated compressors are known for their smooth and quiet operation. The oil lubrication helps reduce noise levels and vibration, resulting in a more comfortable working environment.
3. Maintenance: These compressors require regular oil changes and maintenance to ensure the proper functioning of the lubrication system. The oil filter may need replacement, and the oil level should be regularly checked and topped up.
4. Applications: Oil-lubricated compressors are commonly used in applications that demand high air quality and continuous operation, such as industrial settings, workshops, and manufacturing facilities.
Oil-Free Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-free air compressors do not use oil for lubrication. Instead, they utilize alternative materials, such as specialized coatings, self-lubricating materials, or water-based lubricants, to reduce friction and wear.
2. Performance: Oil-free compressors generally have a higher airflow capacity, making them suitable for applications where a large volume of compressed air is required. However, they may produce slightly more noise and vibration compared to oil-lubricated compressors.
3. Maintenance: Oil-free compressors typically require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated ones. They do not need regular oil changes or oil filter replacements. However, it is still important to perform routine maintenance tasks such as air filter cleaning or replacement.
4. Applications: Oil-free compressors are commonly used in applications where air quality is crucial, such as medical and dental facilities, laboratories, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications. They are also favored for portable and consumer-grade compressors.
When selecting between oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors, consider the specific requirements of your application, including air quality, noise levels, maintenance needs, and expected usage. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and lubrication to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the air compressor.


editor by CX 2023-10-04
China high quality Heavy Duty Trailer 30000lbs Independent Air Bag Suspension Kit Compressor wholesaler
Product Description
Applications
A semi-trailer suspension is an important part connecting the traveling device and the frame of the semi-trailer.
All forces are all transmitted through the suspension system. And the suspension reduces the impact of harsh roads on the vehicle, plays a shock absorption effect, and improves the ride comfort of the vehicle.
Semi-trailer suspensions are widely applied to skeletal trailers, lowbed trailers, flatbed trailers, dump trailers, car transport trailers, oil tank trailers, van trailers, full trailers, wood transport trailers, agricultrucal vehicles, etc. Classification of suspension indlude German series suspensions, American series suspensions, bogie/boogie suspension series, air suspension series, rigid suspension series, CHINAMFG suspensions, ROR suspensions, HENRED suspensions, semi-trailer suspensions, trailer suspensions and agricultural series, etc.
Features
| QC management system | Implementing IATF 16949-2016 | ||||||
| Services quality management system | Implementing ISO 9001-2015 | ||||||
| Warranty | 18 months since shipping date | ||||||
| Quality testing passed | An independent lab in China | ||||||
| Raw material for suspensions | Q235 from China’s TOP-3 steel mills can achieve a longer life under higher loads | ||||||
| Steel plate cutting by | CNC Plasma Cutting Machines | ||||||
| Press forming by | 40-800 ton hydraulic press machines with hundreds of precision molds | ||||||
| Hanger welding by | Automatic CNC welding robots/lines with hundreds of precise fixture toolings | ||||||
| Smooth surface by | Shot-peening | ||||||
| Painting by | Automatic coating line | ||||||
| Producing leaf springs and casting parts by | Ourselves to ensure the lead time and quality are under control | ||||||
| Equalizer bushes | Using taper or greaseless powdered metal ones to be more durable | ||||||
| Arm bushes | Using natural rubber ones to be more durable | ||||||
| Adjustable arms screw by | Galvanized anti-rust treatment | ||||||
| Sets of annual output | 50,000 | 1180 | 441 | 433 | 183 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885711A |
| WDA2223908801 | 1220 | 481 | 473 | 223 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885712A | |
| WDA2253908801 | 1250 | 511 | 503 | 253 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885713A | |
| WDA2164908801 | 1180 | 422 | 414 | 164 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885711B | |
| WDA2204908801 | 1220 | 462 | 454 | 204 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885712B | |
| WDA2234908801 | 1250 | 492 | 484 | 234 | 13,000 * 2 | FW885713B |
WD88.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3185908801 | 1180 | 457 | 448 | 435 | 185 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880301A |
| WDA3225908801 | 1220 | 497 | 488 | 475 | 225 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880302A |
| WDA3255908801 | 1250 | 527 | 518 | 505 | 255 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880303A |
| WDA3166908801 | 1180 | 438 | 429 | 416 | 166 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880301B |
| WDA3206908801 | 1220 | 478 | 469 | 456 | 206 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880302B |
| WDA3236908801 | 1250 | 508 | 499 | 486 | 236 | 13,000 * 3 | FW880303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×7 pcs
-WD86 Type Heavy Duty Suspension Series
WD86.02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA2183908601 | 1180 | 473 | 465 | 183 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865711A |
| WDA2223908601 | 1220 | 513 | 505 | 223 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865712A |
| WDA2253908601 | 1250 | 543 | 535 | 253 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865713A |
| WDA2164908601 | 1180 | 454 | 446 | 164 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865711B |
| WDA2204908601 | 1220 | 494 | 484 | 204 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865712B |
| WDA2234908601 | 1250 | 526 | 518 | 234 | 16,000 * 2 | FW865713B |
WD86.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) |
A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3183908601 | 1180 | 489 | 480 | 467 | 183 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860301A |
| WDA3223908601 | 1220 | 529 | 520 | 507 | 223 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860302A |
| WDA3253908601 | 1250 | 599 | 550 | 537 | 253 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860303A |
| WDA3164908601 | 1180 | 470 | 461 | 448 | 164 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860301B |
| WDA3204908601 | 1220 | 510 | 501 | 588 | 204 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860302B |
| WDA3234908601 | 1250 | 540 | 531 | 518 | 234 | 16,000 * 2 | FW860303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×9 pcs
-WD86 Type Heavy Duty Underslung Suspension Series
WD86.21 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | L4 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA | 495 | 1310 | 1135 | 1165 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.2/1310/250/BQ6/9 |
| WDA | 495 | 1360 | 1160 | 1190 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.2/1360/250/BQ6/9 |
WD86.31 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | L4 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA | 495 | 1310 | 1135 | 1165 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.3/1310/250/BQ6/9 |
| WDA | 495 | 1360 | 1160 | 1190 | 16,000 * 2 | FW86.3/1360/250/BQ6/9 |
Note:
(1) Suitable for round/square axles
(2) Suggested leaf spring: 90×16×9 pcs
-WD68 Type Stamping Suspension Series
WD68.21 AR5 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA244571801 | 440 | 440 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21HHAR05 |
| WDA2415756801 | 415 | 415 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21MMAR05 |
| WDA239571801 | 390 | 390 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21LLAR05 |
| WDA244571802 | 440 | 415 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21HMAR05 |
| WDA2415756802 | 415 | 390 | 11,000 * 2 | FW68.21MLAR05 |
WD68.31 AR5 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA344571801 | 440 | 440 | 440 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31HHHAR05 |
| WDA3415756801 | 415 | 415 | 415 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31MMMAR05 |
| WDA339571801 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.31LLLAR05 |
| WDA344571802 | 440 | 415 | 390 | 16,000 * 2 | FW68.21HMLAR05 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 75×13×8 pcs
-WD66 Type Lightweight Suspension Series
WD66.22 AR5 Tandem (2-axle) Underslung Suspensions
| Model | A1 (mm) | L1 (mm) | L2 (mm) | L3 (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA239571601 | 390 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
| WDA2415756601 | 415 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
| WDA244571601 | 440 | 482.5 | 1245 | 1105 | 10,000 * 2 | FW66.2/1245/390/AR5/3L |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 75×22×3 pcs
-WD20 Type Heavy Duty Suspension Series
WD20.02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA2183157101 | 1180 | 489 | 481 | 183 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25711A |
| WDA2223157101 | 1220 | 529 | 521 | 223 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25712A |
| WDA2253157101 | 1250 | 559 | 551 | 253 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25713A |
| WDA2164157101 | 1180 | 470 | 462 | 164 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25711B |
| WDA | 1220 | 510 | 502 | 204 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25712B |
| WDA2234157101 | 1250 | 540 | 532 | 234 | 20,000 * 2 | FW25713B |
WD20.03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | Height of towing plate (mm) | A1 (mm) | A2 (mm) | A3 (mm) | H (mm) | Axle Loading (kg) | Replacement |
| WDA3183157101 | 1180 | 505 | 496 | 483 | 183 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200301A |
| WDA3223157101 | 1220 | 545 | 536 | 523 | 223 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200302A |
| WDA3253157101 | 1250 | 575 | 566 | 553 | 253 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200303A |
| WDA3164157101 | 1180 | 486 | 477 | 464 | 164 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200301B |
| WDA | 1220 | 526 | 517 | 504 | 204 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200302B |
| WDA3234157101 | 1250 | 556 | 547 | 534 | 234 | 20,000 * 2 | FW200303B |
Note:
(1) Demension “A1, A2, A3”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×16×10 pcs
German type Suspension Series (BPW type)
WDGB02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGB21551001201 | 155 | 490 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGB21551001401 | 155 | 514 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
WDGB03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGB31551001201 | 155 | 490 | 1295 | 615 | 3970 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGB31551001401 | 155 | 514 | 1295 | 615 | 3970 | 100×12×14 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A”: unladen
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×12×12 pcs, 100×14×12 pcs, 100×12×14 pcs
German type Suspension Series (SAF type)
WDGS02 Tandem (2-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGS21551001201 | 155 | 500 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGS21551001401 | 155 | 524 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
WDGS03 Tri (3-axle) Suspensions
| Model | H (mm) | A (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) | Leaf spring |
| WDGS21551001201 | 155 | 500 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×12 |
| WDGS21551001401 | 155 | 524 | 1295 | 615 | 2610 | 100×12×14 |
Note:
(1) Demension “A”: unladen;Note:
(2) Suitable for round/square axles
(3) Suggested leaf spring: 100×12×12 pcs, 100×14×12 pcs, 100×12×14 pcs
Production
Workshops of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Raw material workshops, Components workshops, Mechanical suspension processing workshops, Semi trailer suspensionAssembly workshops, Painting line)
Processes & equipment of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
- Steel Plate Material→ 2. Steel Plate CNC Automatic Cutting→ 3. Hangers punching→ 4. Hangers Forming→ 5. Hangers Welding→ 6. Sleeve(A & B) Welding→ 7. Shot Peening→ 8. Painting→ 9. Laser marking→ 10. Assembling→ 11. Packing→ 12. Warehousing)
Products and logistics of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Mechanical suspension final production, Suspension hangers, Components of semi trailer suspensions, Suspension warehousing, Suspension packing, trailer suspension container loading)
Other types of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Germany BPW type mechanical suspension, Germany SAF type mechanical suspension, American CHINAMFG type suspension with square beam, American CHINAMFG underslung type suspension with square beam, American CHINAMFG type suspension with round beam, American CHINAMFG underslung type suspension with round beam)
Other types of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(YTE casting type suspension, ROR casting type suspension, Henred Fruehauf type suspension, Agricultural trailer suspension)
Components
Components & spare parts of CHINAMFG Autoparts semi trailer suspensions:
(Font hangers, Middle hangers, Rear hangers, Supension equalizers, Equalizer pins, Leaf springs, Fix torques, Adjustable torques, U-bolts, etc.)
Besides trailer mechanical suspensions, CHINAMFG Autoparts also supply different types of semi trailer components as below:
| After-sales Service: | 18 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18 Months |
| Material: | Steel |
| Certification: | ISO/TS16949, ISO9001 |
| Car Make: | Benz, BMW, Toyota, Jeep, Nissan, Ford, Volvo, Mazda |
| Position: | Rear |
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for shipbuilding and maritime applications?
Air compressors are widely used in shipbuilding and maritime applications for a variety of tasks and operations. The maritime industry relies on compressed air for numerous essential functions. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are employed in shipbuilding and maritime applications:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Air compressors are extensively used to power pneumatic tools and equipment in shipbuilding and maritime operations. Pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches, drills, grinders, sanders, and chipping hammers require compressed air to function. The versatility and power provided by compressed air make it an ideal energy source for heavy-duty tasks, maintenance, and construction activities in shipyards and onboard vessels.
2. Painting and Surface Preparation:
Air compressors play a crucial role in painting and surface preparation during shipbuilding and maintenance. Compressed air is used to power air spray guns, sandblasting equipment, and other surface preparation tools. Compressed air provides the force necessary for efficient and uniform application of paints, coatings, and protective finishes, ensuring the durability and aesthetics of ship surfaces.
3. Pneumatic Actuation and Controls:
Air compressors are employed in pneumatic actuation and control systems onboard ships. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic valves, actuators, and control devices that regulate the flow of fluids, control propulsion systems, and manage various shipboard processes. Pneumatic control systems offer reliability and safety advantages in maritime applications.
4. Air Start Systems:
In large marine engines, air compressors are used in air start systems. Compressed air is utilized to initiate the combustion process in the engine cylinders. The compressed air is injected into the cylinders to turn the engine’s crankshaft, enabling the ignition of fuel and starting the engine. Air start systems are commonly found in ship propulsion systems and power generation plants onboard vessels.
5. Pneumatic Conveying and Material Handling:
In shipbuilding and maritime operations, compressed air is used for pneumatic conveying and material handling. Compressed air is utilized to transport bulk materials, such as cement, sand, and grain, through pipelines or hoses. Pneumatic conveying systems enable efficient and controlled transfer of materials, facilitating construction, cargo loading, and unloading processes.
6. Air Conditioning and Ventilation:
Air compressors are involved in air conditioning and ventilation systems onboard ships. Compressed air powers air conditioning units, ventilation fans, and blowers, ensuring proper air circulation, cooling, and temperature control in various ship compartments, cabins, and machinery spaces. Compressed air-driven systems contribute to the comfort, safety, and operational efficiency of maritime environments.
These are just a few examples of how air compressors are utilized in shipbuilding and maritime applications. Compressed air’s versatility, reliability, and convenience make it an indispensable energy source for various tasks and systems in the maritime industry.
.webp)
What is the role of air compressors in manufacturing and industrial processes?
Air compressors play a crucial role in various manufacturing and industrial processes, providing a reliable source of compressed air that powers a wide range of equipment and tools. Here are some key roles of air compressors in manufacturing and industrial settings:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Air compressors power a wide range of pneumatic tools and equipment used in manufacturing processes. These tools include impact wrenches, air drills, sanders, grinders, nail guns, and spray guns. Compressed air provides the necessary force and energy for these tools, enabling efficient and precise operations.
2. Automation and Control Systems:
Compressed air is used in automation and control systems within manufacturing facilities. Pneumatic actuators and valves use compressed air to control the movement of machinery and components. These systems are widely used in assembly lines, packaging operations, and material handling processes.
3. Air Blowing and Cleaning:
Compressed air is employed for blowing and cleaning applications in manufacturing and industrial processes. Air blowguns and air nozzles are used to remove debris, dust, and contaminants from surfaces, machinery, and products. Compressed air is also used for drying, cooling, and purging operations.
4. Air Separation and Gas Generation:
Air compressors are used in air separation plants to generate industrial gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. These gases are essential for various industrial processes, including metal fabrication, chemical production, and food packaging.
5. HVAC Systems:
Compressed air is utilized in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It powers pneumatic actuators for damper control, pneumatic controls for pressure regulation, and pneumatic valves for flow control in HVAC applications.
6. Air Compression for Storage and Transport:
Compressed air is used for storage and transport purposes in manufacturing and industrial settings. It is often used to pressurize storage tanks or containers that hold gases or liquids. Compressed air also facilitates the transfer of materials through pipelines and pneumatic conveying systems.
7. Process Instrumentation:
Compressed air is utilized in process instrumentation and control systems. It powers pneumatic instruments such as pressure gauges, flow meters, and control valves. These instruments play a critical role in monitoring and regulating various parameters in industrial processes.
8. Material Handling and Pneumatic Conveying:
In manufacturing and industrial facilities, compressed air is used for material handling and pneumatic conveying systems. It enables the movement of bulk materials such as powders, granules, and pellets through pipelines, facilitating efficient and controlled material transfer.
Overall, air compressors are vital components in manufacturing and industrial processes, providing a versatile and efficient source of power for a wide range of applications. The specific role of air compressors may vary depending on the industry, process requirements, and operational needs.
.webp)
What is the difference between a piston and rotary screw compressor?
Piston compressors and rotary screw compressors are two common types of air compressors with distinct differences in their design and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between these two compressor types:
1. Operating Principle:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors, also known as reciprocating compressors, use one or more pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress air. The piston moves up and down within a cylinder, creating a vacuum during the intake stroke and compressing the air during the compression stroke.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors utilize two intermeshing screws (rotors) to compress air. As the male and female screws rotate, the air is trapped between them and gradually compressed as it moves along the screw threads.
2. Compression Method:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors achieve compression through a positive displacement process. The air is drawn into the cylinder and compressed as the piston moves back and forth. The compression is intermittent, occurring in discrete cycles.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors also employ a positive displacement method. The compression is continuous as the rotating screws create a continuous flow of air and compress it gradually as it moves along the screw threads.
3. Efficiency:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors are known for their high efficiency at lower flow rates and higher pressures. They are well-suited for applications that require intermittent or variable air demand.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are highly efficient for continuous operation and are designed to handle higher flow rates. They are often used in applications with a constant or steady air demand.
4. Noise Level:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors tend to generate more noise during operation due to the reciprocating motion of the pistons and valves.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are generally quieter in operation compared to piston compressors. The smooth rotation of the screws contributes to reduced noise levels.
5. Maintenance:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors typically require more frequent maintenance due to the higher number of moving parts, such as pistons, valves, and rings.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance requirements. They often have longer service intervals and can operate continuously for extended periods without significant maintenance.
6. Size and Portability:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors are available in both smaller portable models and larger stationary units. Portable piston compressors are commonly used in construction, automotive, and DIY applications.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are typically larger and more suitable for stationary installations in industrial and commercial settings. They are less commonly used in portable applications.
These are some of the key differences between piston compressors and rotary screw compressors. The choice between the two depends on factors such as required flow rate, pressure, duty cycle, efficiency, noise level, maintenance needs, and specific application requirements.


editor by CX 2023-10-03
China D3 Air Suspension Compressor for BMW A8/ S8 D3 OEM 4e0616005D 4e0616005f 4e0616005h 4154033080 air compressor for car
Product Description
D3 Air Suspension Compressor For BMW A8/ S8 D3 OEM 4E0616
Main Items:Air Spring,Convoluted Air Spring,Industrial Air Springs,Air Suspension Spring,Air Compressor,Air Valve,Bus Rubber Bellows,Truck & Trailer Air Bags,Cabin Air Shock,Electric powered H2o Pump
Specifications
| Type | Air Compressor | Product NO. | 52 | Construction Year: |
2 |
A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Doorway | four.2L 4172CC V8 Fuel DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gas DOHC Normally Aspirated | |||||
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 D | A8 Quattro | L Furthermore Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC Naturally Aspirated | |||
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | four.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC By natural means Aspirated | |||
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 H | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Doorway | four.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC In a natural way Aspirated | |||
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 | A8 Quattro | Foundation Sedan 4-Doorway | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gas DOHC Naturally Aspirated | |||
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC In a natural way Aspirated | |||
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 D | A8 Quattro | Furthermore Sedan 4-Doorway | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC By natural means Aspirated | |||
| 2003 | Audi | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Doorway | four.2L 4172CC V8 Fuel DOHC In a natural way Aspirated | ||||
| 2003 | Audi | 415457160 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC Normally Aspirated | |||
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | four.2L 4172CC V8 Gasoline DOHC In a natural way Aspirated | |||
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 Fuel DOHC By natural means Aspirated |
|
US $1-199 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Rubber and Aluminum, Aluminum and Steel |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO/TS16949, ISO9001 |
| Car Make: | Audi |
| Position: | Rear |
| OEM: | Yes |
| Type: | Air Suspension Compressor |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 199/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Type | Air Compressor | Model NO. | 520011 |
| Car make |
Audi |
Package |
Strong Cartons |
| Use |
Inflate Air Spring |
Warranty | One year |
| Rubber type | Natural rubber | Place of origin | Guangzhou China (mainland) |
| Manufacturer part NO. |
4E0616005D 4E0616005F 4E0616005H 4E0616007 4E0616007B 4E0616007D WABCO 4154033080 |
Construction Year: |
2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010 |
###
| Year | Audi | OEM | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2010 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC 255Cu. In. V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2010 | Audi | 4E0616005H | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007D | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | WABCO 4154033080 | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 F | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 H | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 B | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 415 403 116 0 | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4154031160 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0616005D | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616005H | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007 | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007D | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | WABCO 4154033080 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 D | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 H | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 D | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2003 | Audi | 415 403 116 0 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2003 | Audi | 4154031160 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
|
US $1-199 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Rubber and Aluminum, Aluminum and Steel |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO/TS16949, ISO9001 |
| Car Make: | Audi |
| Position: | Rear |
| OEM: | Yes |
| Type: | Air Suspension Compressor |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 199/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Type | Air Compressor | Model NO. | 520011 |
| Car make |
Audi |
Package |
Strong Cartons |
| Use |
Inflate Air Spring |
Warranty | One year |
| Rubber type | Natural rubber | Place of origin | Guangzhou China (mainland) |
| Manufacturer part NO. |
4E0616005D 4E0616005F 4E0616005H 4E0616007 4E0616007B 4E0616007D WABCO 4154033080 |
Construction Year: |
2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010 |
###
| Year | Audi | OEM | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2010 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC 255Cu. In. V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2010 | Audi | 4E0616005H | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | 4E0616007D | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Audi | WABCO 4154033080 | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 F | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 H | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 B | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 415 403 116 0 | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4154031160 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4163CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0616005D | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616005H | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007 | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Audi | 4E0616007D | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | WABCO 4154033080 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 D | A8 Quattro | L Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Audi | 4E0 616 005 H | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 B | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Audi | 4E0 616 007 D | A8 Quattro | Plus Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2003 | Audi | 415 403 116 0 | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2003 | Audi | 4154031160 | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005D | A8 Quattro | Base Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2002 | Audi | 4E0616005F | A8 Quattro | L Sedan 4-Door | 4.2L 4172CC V8 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
Choosing an Air Compressor
Considering a new Air Compressor? Here are some tips to make the decision easier. Learn the pros and cons of each type, including the differences between oil-injected and oil-free models, single stage and positive displacement. In addition, learn more about the different technologies that are available for your air compressor. It is important to choose an appropriate unit for the type of work you do. Here are some of the best compressors available today.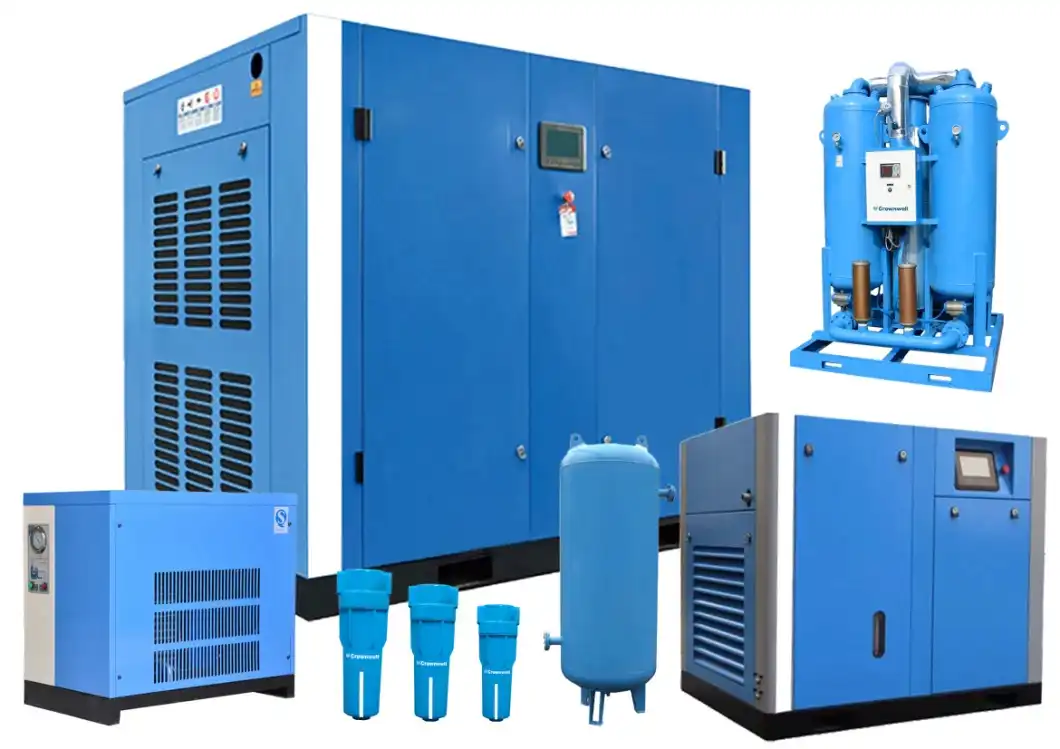
Positive displacement
There are several different types of air compressors, but most are positive displacement air compressors. They use a rotary or reciprocating component to compress air. The reciprocating component compresses air by reducing the volume of the chamber. Positive displacement compressors are used in bicycle pumps, chemical plants, and refrigerators. Positive displacement air compressors use multiple inlet ports. Despite the various types, the principle of operation remains the same.
Another type of positive displacement air compressor is a reciprocating piston. The piston inside a cylinder moves up and down, causing the compressed air to fill the upper part of the cylinder. These air compressors are used in a variety of different applications, including blowing bottles and gas pipelines. These air compressors can be water-cooled, lubricated, or non-lubricated. Different types have different capacities and air pressures.
A positive displacement flowmeter uses a rotating chamber that divides continuous fluid into discrete portions. The number of times the chamber is filled and discharged can be used to estimate the flow rate. The rotation speed of the measuring chamber is directly proportional to the flow rate. The drawbacks of this type of positive displacement flowmeter are that it is prone to jamming. If the fluid contains particles, it may be too thick for the meter to determine flow rate.
A negative displacement air compressor was invented in 1860 and is the oldest type of compressor. It uses two lobes positioned in a circular cavity. One rotor is connected to an engine, while the other pushes the other one to spin in the opposite direction. Negative displacement compressors are low-maintenance, but they do require more precision. They are often used in nuclear power plants because they use the kinetic energy of the rotating elements to produce pressure.
Oil-injected
Oil-flooded or oil-injected air compressors use liquid to seal and lubricate moving parts and reduce noise. Oil-flooded air compressors are effective for a variety of pneumatic tools and accessories. Some models have a thermostat that controls the amount of oil used during operation. Other types of oil-flooded air compressors are piston-type models. Here is an overview of the basic differences between these two air compressors.
An oil-injected air compressor is more expensive than a comparable oil-free air compressor, but its advantages far outweigh its disadvantages. An oil-free compressor is quieter, requires less maintenance, and has a lower price tag. It also offers a greater degree of air purity. A number of other advantages may also make this type of air compressor the better choice for many industrial settings. If you need a high-pressure compressor in a tight space, consider the benefits of an oil-free system.
Oil-injected air compressors require more maintenance than oil-free models. Both types of air compressors offer similar capacity and ISO 8573-1 Class 0 and 1-2 purity, but the oil-injected systems require more air-treatment components. They require an activated carbon filter and coalescing filter. Oil-injected air compressors will likely remain the standard for industrial air compressors for many years. And since their performance and efficiency are comparable, it may be worthwhile to invest in some point-of-use air treatment.
Both types of air compressors have their benefits. However, choosing between oil-free and oil-injected air compressors is not as straightforward as you might think. Whichever type you choose, make sure it will meet your needs. The benefits of an oil-injected air compressor outweigh their disadvantages. In general, oil-injected air compressors are more durable and can last longer than oil-free models. The only downside is their higher price.
Oil-free
When choosing an air compressor for your company, you’ll need to determine what it is going to be used for. For example, if you’re planning on using it to power multiple workers, you should consider getting an oil-free compressor. An oil-free compressor, on the other hand, is quieter and can power several workers at a time. If you’re a contractor, the most important consideration will be the type of jobs you’ll be doing. Higher air pressure means greater demand for air flow, and more pressure can damage the equipment.
Oil-free compressed air is certified 100% free of contaminants. Technically, oil-free air is not completely free of foreign matter, but it is extremely low within the limits of practical air quality. A technically oil-free air compressor might have a total oil level of 0.003 mg/m3. If you’re in need of a technically oil-free air compressor, you must install an air treatment equipment after your current compressor.
If you’re in the manufacturing industry, a good oil-free air compressor will save you money and reduce your environmental impact. Many of these tools require air compressors to work, and this equipment will ensure that they don’t get contaminated. To buy the best oil-free compressor, you should learn a bit about the different terms used by compressor repair companies. ACFM, for example, is the amount of air that can be compressed in one minute at rated conditions.
When you’re using an oil-free air compressor, you should know that the overall life of the device will be much shorter. Compared to an oil-flooded rotary screw air compressor, an oil-free compressor typically has a lifespan of 50 thousand hours. But it’s important to understand that this type of compressor can still cause damage to piping and processes. Therefore, you should choose an oil-free compressor when you need to clean air for your business.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor, also known as a piston air compressor, compresses air only once before storing it in a cylinder. This stored air has enough energy to power a variety of pneumatic tools, such as screwdrivers, chisels, and wrenches. These units are also ideally suited for low-flow applications and are widely used in gas stations, auto shops, and various manufacturing plants.
A single-stage air compressor uses two valves – one for inlet and one for outlet – to transfer compressed air. Both valves are actuated by springs. The inlet valve has a slight curvature to provide protection from damage. The compressor’s outlet valve opens when the pressure in the cylinder is higher than the pressure in the storage tank. The piston moves very quickly inside the cylinder, exerting a high amount of force throughout the compression process. This high piston speed is a common cause of compressor wear and tear.
A single-stage air compressor is ideal for smaller tradesmen and small construction crews. Its lightweight and compact design make it easier to transport and store. While it may be tempting to buy the first cheap air compressor you see, it’s important to balance the price against performance to choose the right air compressor for your needs. The best single-stage air compressor is one that provides excellent performance and durability. Its two-stage counterpart is designed for larger construction teams and large applications.
The main difference between a single-stage and a two-stage air compressor lies in their capacity. A single-stage air compressor compresses air only once and delivers it into the storage tank, while a two-stage compressor compresses it twice, creating double the pressure. Because of this, single-stage air compressors are cheaper and versatile than their counterparts, which means that they can be used for multiple purposes.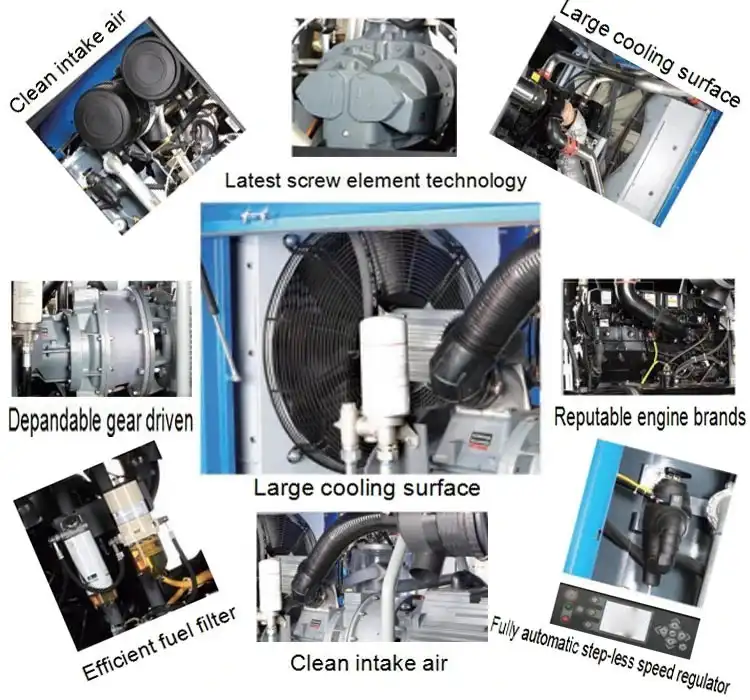
Low-noise
A low-noise air compressor is a type of industrial compressor that is less noisy than regular air compressors. These are generally smaller machines designed for smaller factories and workshops with a few to several employees. They are designed to handle mid-weight volumes of compressed air per day. This type of compressor is especially useful for smaller manufacturing businesses that need to produce compressed air for medical applications. Small breweries can also benefit from the low-noise capabilities of these compressors.
Low-noise air compressors come in various sizes and features. For smaller jobs, you can purchase a one-gallon model that is lightweight and portable. For larger jobs, you can purchase one with a larger tank that can provide more pressure for longer jobs. However, a larger tank will make the compressor heavier and harder to transport. To avoid this, make sure to check the size of the tank and how much power it can handle.
Considering a low-noise air compressor for your business? If so, you’ve come to the right place. There are a variety of affordable and dependable low-noise options to choose from. A CAT 10020C, for example, is designed to provide high-volume air to many outlets at once. A CAT 10020C comes with a 10-gallon tank, wheels, and a carrying handle.
Noise levels can also affect the productivity of employees. When employees work with air compressors in close proximity to each other, they may develop tinnitus. If employees are free from tinnitus because of the loud noise, they are likely to work more efficiently. Moreover, it will be easier for them to focus and communicate efficiently. If you need a compressor, a low-noise one is an excellent choice.


editor by czh 2022-12-31